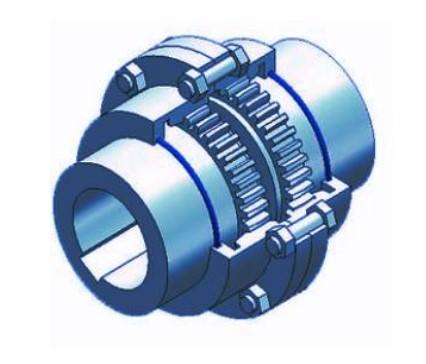
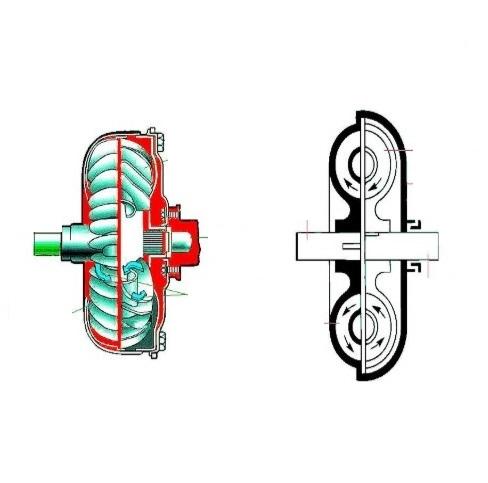
What Are Couplings?
Couplings are mechanical devices used to connect two shafts together at their ends for the purpose of transmitting power. They are essential components in various machinery and industrial applications, ensuring smooth operation, accommodating misalignment, reducing shock loads, and protecting against overloads. At our company, we offer a wide range of high-quality couplings designed to meet diverse industrial needs, from standard applications to specialized environments.
Types of Couplings We Offer
Our product line includes several types of couplings, each suited for specific requirements:
-
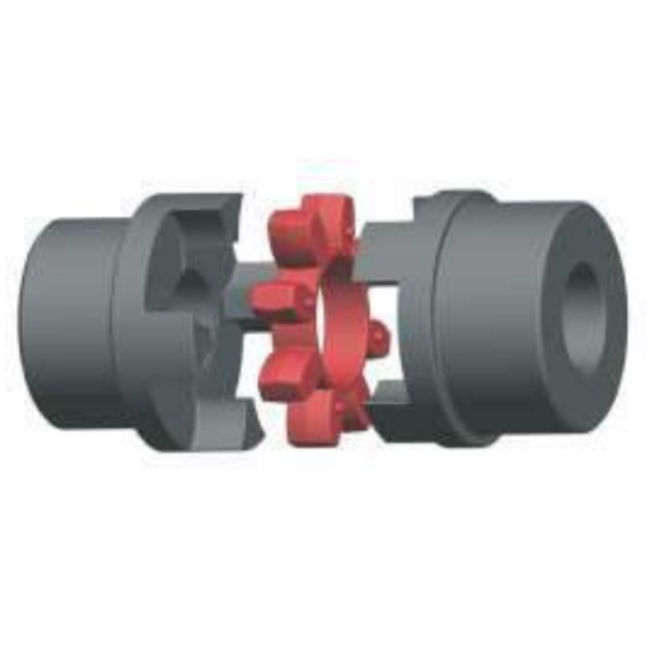
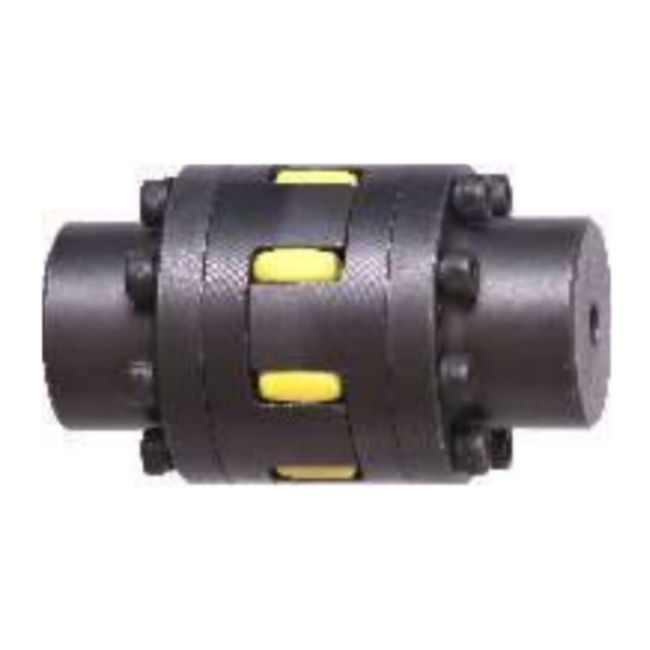
Flexible Couplings: These allow for angular, parallel, and axial misalignment between shafts. Examples include jaw couplings, gear couplings, and disc couplings.
-
Rigid Couplings: Used where precise alignment is required, such as in sleeve couplings or flanged couplings, with no flexibility for misalignment.
-
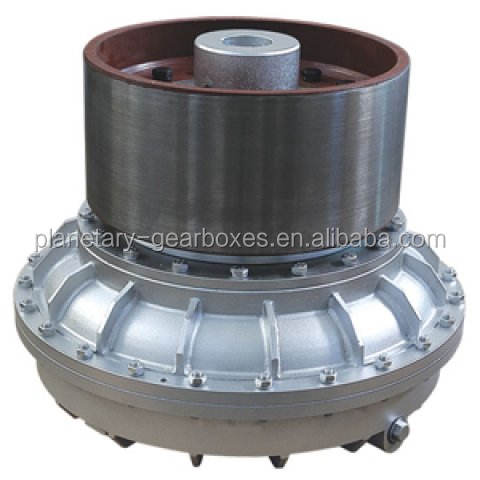
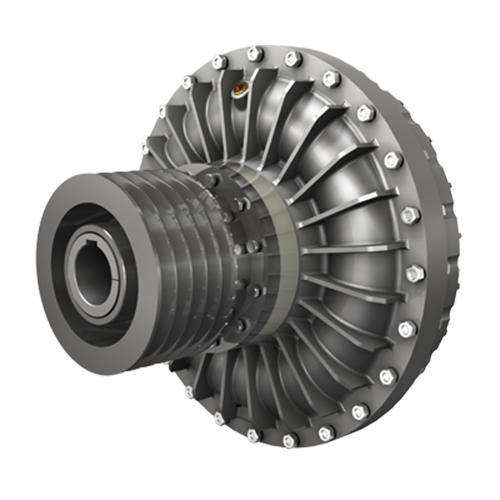
Fluid Couplings: Utilize hydraulic fluid to transmit power, providing smooth acceleration and overload protection, commonly found in conveyors and crushers.
-
Magnetic Couplings: Employ magnetic fields to transfer torque without physical contact, ideal for hermetic sealing in pumps and mixers.
-
Universal Joints (U-Joints): Allow for high degrees of angular misalignment, often used in automotive and aerospace industries.
Key Product Parameters and Specifications
To help you select the right coupling for your application, here are detailed parameters for our popular models. All our couplings are manufactured to international standards, ensuring reliability and performance.
General Parameters Table
|
Parameter
|
Description
|
Typical Values/Range
|
|
Bore Diameter
|
The inner diameter of the coupling hub that fits onto the shaft.
|
10 mm to 200 mm
|
|
Torque Capacity
|
Maximum torque the coupling can transmit without failure.
|
Up to 50,000 Nm
|
|
Speed Rating
|
Maximum rotational speed allowed for safe operation.
|
Up to 10,000 RPM
|
|
Misalignment Tolerance
|
Ability to accommodate angular, parallel, and axial misalignment.
|
Angular: ±3°, Parallel: ±2 mm, Axial: ±4 mm
|
|
Material
|
Common materials used for construction, such as steel, aluminum, or composite.
|
Steel (high-strength), Aluminum (lightweight), Nylon (for electrical insulation)
|
|
Temperature Range
|
Operating temperature limits for the coupling.
|
-40°C to +150°C
|
|
Backlash
|
The amount of free movement between engaged components; low backlash is critical for precision applications.
|
As low as 0.05° for high-precision models
|
|
Weight
|
Mass of the coupling, important for balancing and installation.
|
0.5 kg to 50 kg, depending on size and material
|
Specific Product Models and Their Parameters
Here is a table showcasing some of our best-selling coupling models with their key specifications:
|
Model Number
|
Type
|
Bore Range (mm)
|
Max Torque (Nm)
|
Max Speed (RPM)
|
Material
|
Applications
|
|
CPL-100
|
Jaw Coupling
|
12-40
|
500
|
6,000
|
Aluminum / Nylon
|
Pumps, conveyors, general machinery
|
|
CPL-200
|
Gear Coupling
|
20-100
|
20,000
|
5,000
|
Steel
|
Heavy-duty industrial equipment, rolling mills
|
|
CPL-300
|
Disc Coupling
|
15-80
|
10,000
|
8,000
|
Stainless Steel
|
High-speed turbines, compressors
|
|
CPL-400
|
Magnetic Coupling
|
10-50
|
200
|
4,000
|
Composite / Neodymium
|
Chemical pumps, mixers where sealing is critical
|
|
CPL-500
|
Fluid Coupling
|
30-150
|
50,000
|
3,000
|
Cast Iron / Steel
|
Mining equipment, crushers, conveyors
|
FAQs About Couplings
Here are some frequently asked questions about couplings, answered in detail to help you make informed decisions.
What is the main purpose of a coupling in machinery?
Couplings are used to connect two shafts to transmit power while accommodating misalignment, reducing vibration, and providing overload protection. They ensure efficient power transfer and prolong the life of machinery by minimizing stress on components.
How do I choose the right coupling for my application?
Selecting the right coupling depends on factors such as torque requirements, speed, type of misalignment (angular, parallel, axial), environmental conditions (temperature, humidity), space constraints, and whether backlash is acceptable. Consult our parameter tables and consider consulting with an engineer for complex applications.
What is the difference between flexible and rigid couplings?
Flexible couplings can accommodate misalignment and absorb shocks, making them suitable for applications where shafts are not perfectly aligned. Rigid couplings require precise alignment and are used where no movement is desired, such as in precision instruments, but they do not handle misalignment well.
Can couplings be used in high-temperature environments?
Yes, many couplings are designed for high-temperature operations. For example, steel couplings can handle up to 150°C, while special materials like certain composites or coatings can extend this range. Always check the temperature rating in the product specifications.
How often should couplings be maintained or replaced?
Maintenance intervals depend on the type of coupling and operating conditions. Generally, inspect couplings every 6-12 months for wear, misalignment, or damage. Flexible elements in jaw or disc couplings may need replacement more frequently, while rigid couplings require less maintenance but should be checked for alignment issues.
What is backlash in couplings, and why is it important?
Backlash refers to the slight movement or play between mating components in a coupling. In precision applications like robotics or CNC machines, low backlash is crucial to avoid positioning errors. Our high-precision couplings offer backlash as low as 0.05° for such needs.
Are there couplings suitable for corrosive environments?
Absolutely. We offer couplings made from stainless steel, aluminum with protective coatings, or non-metallic materials like nylon that resist corrosion. These are ideal for industries like chemical processing, marine, or food and beverage where exposure to moisture or chemicals is common.
Can I customize a coupling for specific shaft sizes or torque needs?
Yes, we provide customization services for bore sizes, materials, and torque capacities to meet unique application requirements. Contact our sales team with your specifications, and we can engineer a solution tailored to your needs.
What are the advantages of magnetic couplings?
Magnetic couplings offer contactless torque transmission, which eliminates wear and tear, reduces maintenance, and provides hermetic sealing to prevent leaks. They are perfect for applications involving hazardous fluids or where isolation is needed, such as in pumps for aggressive chemicals.
How do fluid couplings work, and where are they commonly used?
Fluid couplings use hydraulic fluid to transmit power between shafts, allowing smooth start-ups and protecting against overloads by slipping under excessive load. They are commonly used in heavy machinery like conveyors, crushers, and automotive transmissions to reduce shock loads and improve efficiency.